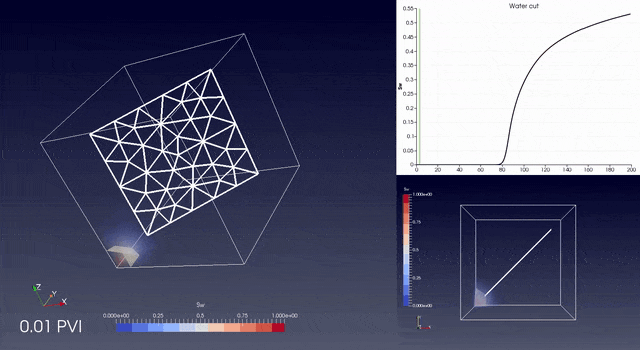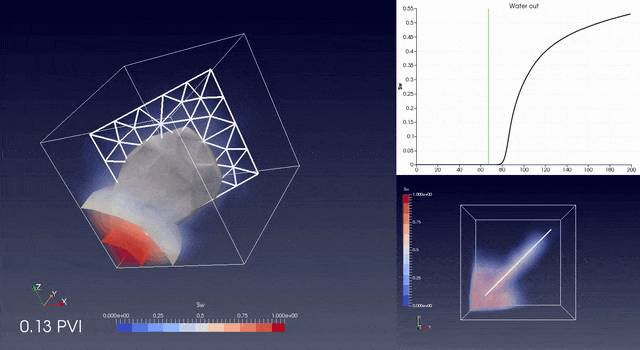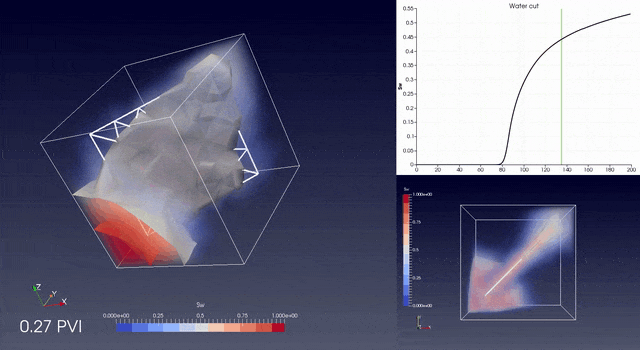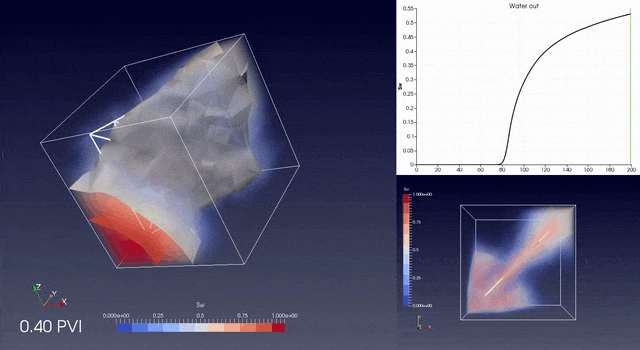
RINGFlow is a Control Volume / Finite Element library to simulate flow in fractured porous media on unstructured grids.
The library contains tools for accurate upscaling from tetrahedral meshes to non aligned and non matching grids.
More information are available in the 2024 training.
This code computes the smooth equivalent medium of any (meshable) geological model for the elastic wave equation. The upscaling method behind the code is the non-periodic homogenization. This method asks to solve an elastostatic problem, which is achieved using a tetrahedral Finite Element Analysis. The result is then smoothed according to the minimum wavelength to be propagated. The obtained medium usually is anisotropic; it can be used in any wave equation solver handling anisotropic heterogeneous media.
SCAR is an external library for generating, repairing, simplifying 2D structural models. SCAR means Simplification, Creation and Automatic Repair.
The main functionality of the SCAR library is the simplification and repair of geological models (available in 2D). But SCAR provides many useful utilities for 2D geological models: conversion of models from one file format to another one, generation of triangular meshes (need other external libraries), remeshing, computation of statistics on mesh quality and model complexity, ...
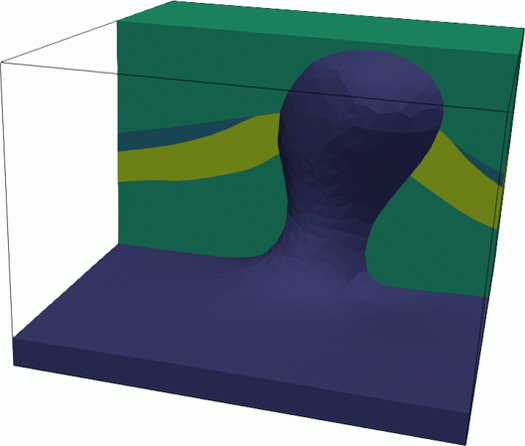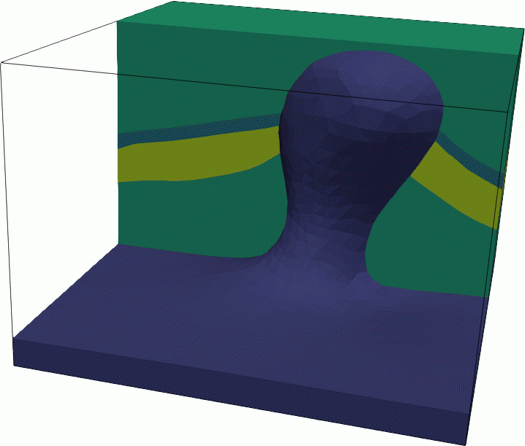
LUMOS is a trianglar and tetrahedral remeshing library which aims at enabling the robust insertion of implicit geological surfaces into existing geological models. This serves two purposes:
- Incremental geological model building,
- Modeling of topological and large geometric uncertainties in geomodeling.
LUMOS was primarily developed by Capucine Legentil. this C++ / Python library is built on top of mmg.
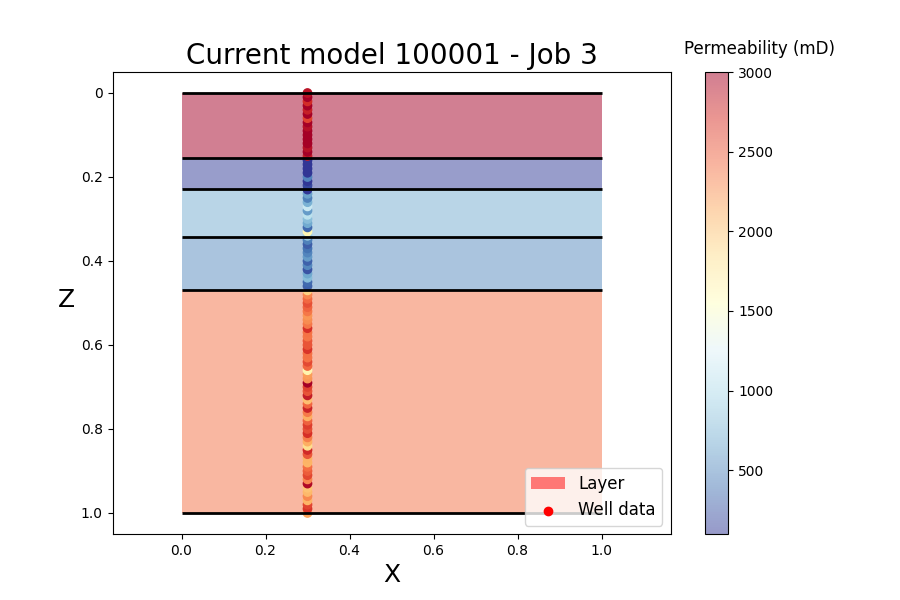
Transdimensional inversion of flow data (TIFlow) is a library to perform transdimensional inversions in history matching problems. In contrast to Bayesian sequential modelling in which permeability values are inferred in a fixed reservoir geometry, TIFlow allows transdimensional Monte Carlo methods based on a reversible jump Markov chain Monte Carlo algorithm (RJMCMC). These approaches are a way to solve the inverse problem with a self-adaptive geological parameterization in which the number of model parameters is unknown.
The code considers a 2D layered reservoir model. The number of geological layers is variable and the algorithm will converge towards the appropriate reservoir parameter (permeability property) and reservoir geometry (number and location of layer interfaces), using flow data and static reservoir data.
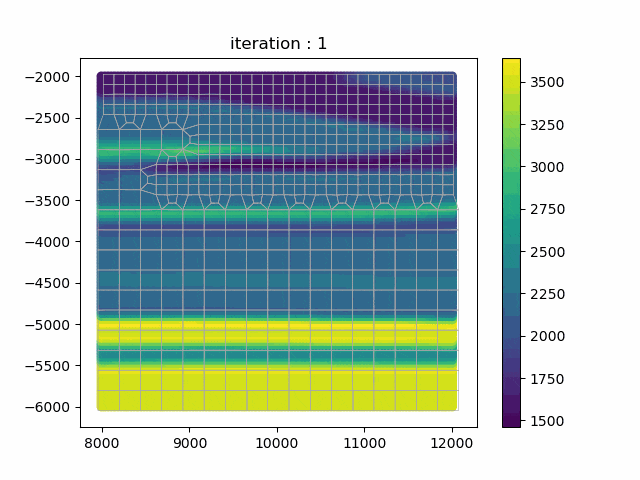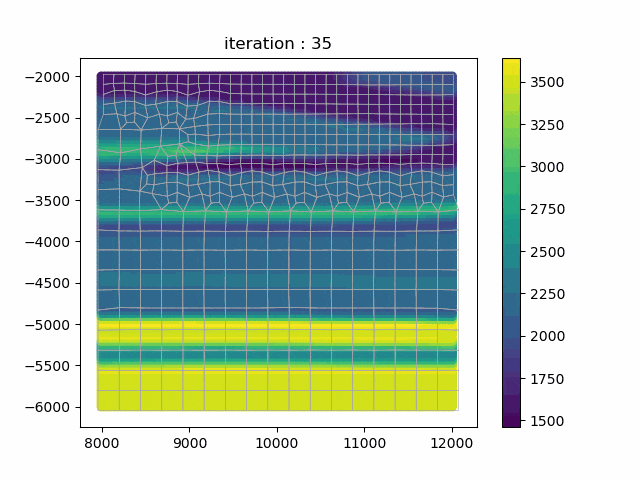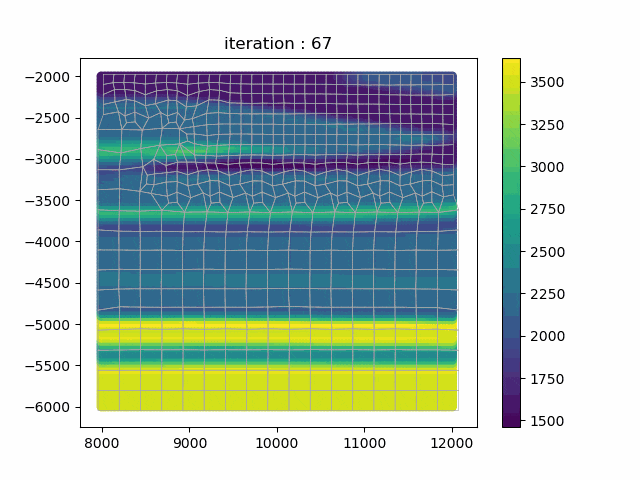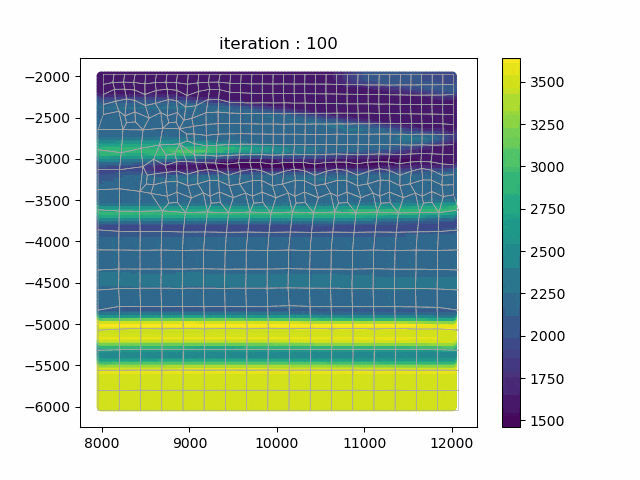
SmoothQuad is a library for 2D meshing and optimization of homogenized medium for seismic simulations. implements mesh optimization algorithm with a modified cotangent Laplacian algorithm in order to bring each node in a position in which the wave simulation would perform better (maximizing the Δx/Δt in each element). The mesh is returned in msh 2.2 format and the code provides some methods to integrate it and the homogenized model into the SpecFem2D simulator.
This library is primarily being developed by Marius Rapenne in C++/Python/Fortran in the frame of his PhD thesis on Adaptive Homogenization for Seismic Risk Estimation.
The code is avalable on Github for sponsors here.
VorteXLib is an external library for generating unstructured meshes conformal to 3D structural models.
Geological interfaces play a significant role in the subsurface physical behavior. Capturing the interface geometry with accuracy in the mesh is then important to reduce numerical errors and approximations. Unstructured meshes are more flexible to represent complex geometries. VorteXLib offers two workflows to generate unstructured meshes conformal to 3D geological models.
